We are trying and searching the authentic solution about back pain treatment and asking various question for self as, Back pain how it Diagnosis and treatment & How to remove back pain or How can I avoid back pain and What is the best back pain relief management so we should know. Back pain For many of us, it’s a quiet battle we fight every day. It starts as a dull ache, maybe after a long day at work or a restless night’s sleep.
So this article try to explain you Very First Line About Back Pain because Not All Back Pain is the Same Understanding the Differences Can Change Lives could save you from a lifetime of unnecessary suffering. Back pain can be a signal for deeper, more complex conditions. But here’s the truth: Your pain matters. Back pain is the result of degeneration wear and tear from aging, known as spondylosis. It’s the body’s quiet cry as the spine begins to break down over time. Others may be dealing with the sharp sting of inflammation, like in the case of spondylitis, a condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own spine.
The pain from spondylitis can feel unrelenting, especially in the early morning when your body feels its stiffest. The truth is, these conditions aren’t the same, and they shouldn’t be treated the same way. You deserve answers, You deserve care And most importantly, you deserve relief, Please, talk to your doctor. Take that first step towards understanding what your body is trying to tell you. Because not all back pain is the same—and understanding yours can change everything in this article i am going to explain you conservative approach for degenerative low back pain called spondylosis.
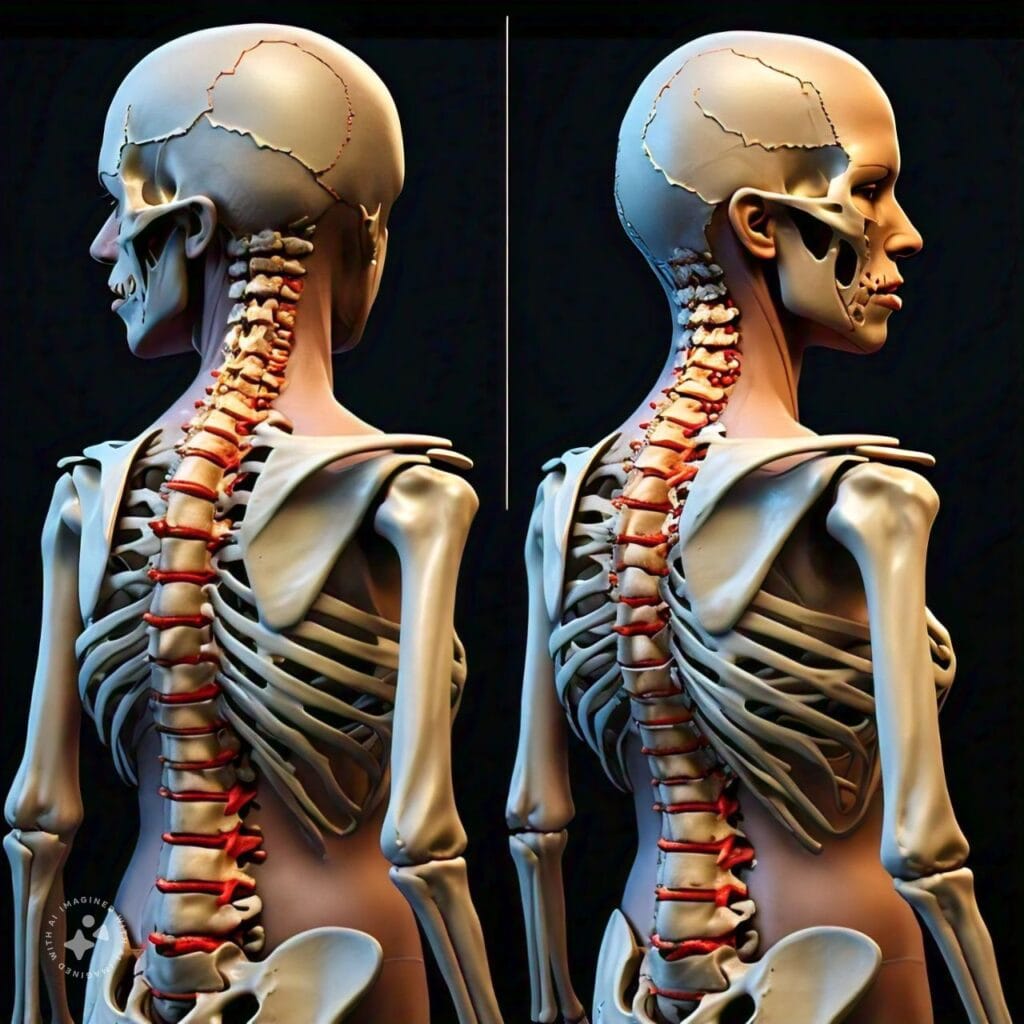
The Difference Between Spondylosis and Spondylitis
In today’s fast-paced world, back pain and spinal issues are becoming alarmingly common. Among the various conditions affecting the spine, spondylosis and spondylitis are often confused. While they may sound similar and both relate to problems with the spine, these two conditions have distinct causes, symptoms, and treatment methods. Understanding the difference between spondylosis and spondylitis is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
In this article, we’ll break down the key differences between spondylosis and spondylitis, explain their symptoms, causes, treatment options, and offer advice for managing these conditions. By the end of this piece, you will have a clearer understanding of which condition may be impacting your life or the life of a loved one, and the steps you can take for relief.
Very first line about Back Pain – What is Spondylosis?
Spondylosis is a degenerative condition that affects the spine, particularly the discs and joints between the vertebrae. It is most commonly associated with aging and often referred to as spinal osteoarthritis. As we age, the discs in our spine lose water content and shrink, leading to wear and tear on the bones and cartilage. This degeneration can result in pain, stiffness, and sometimes the compression of nearby nerves, leading to additional symptoms.
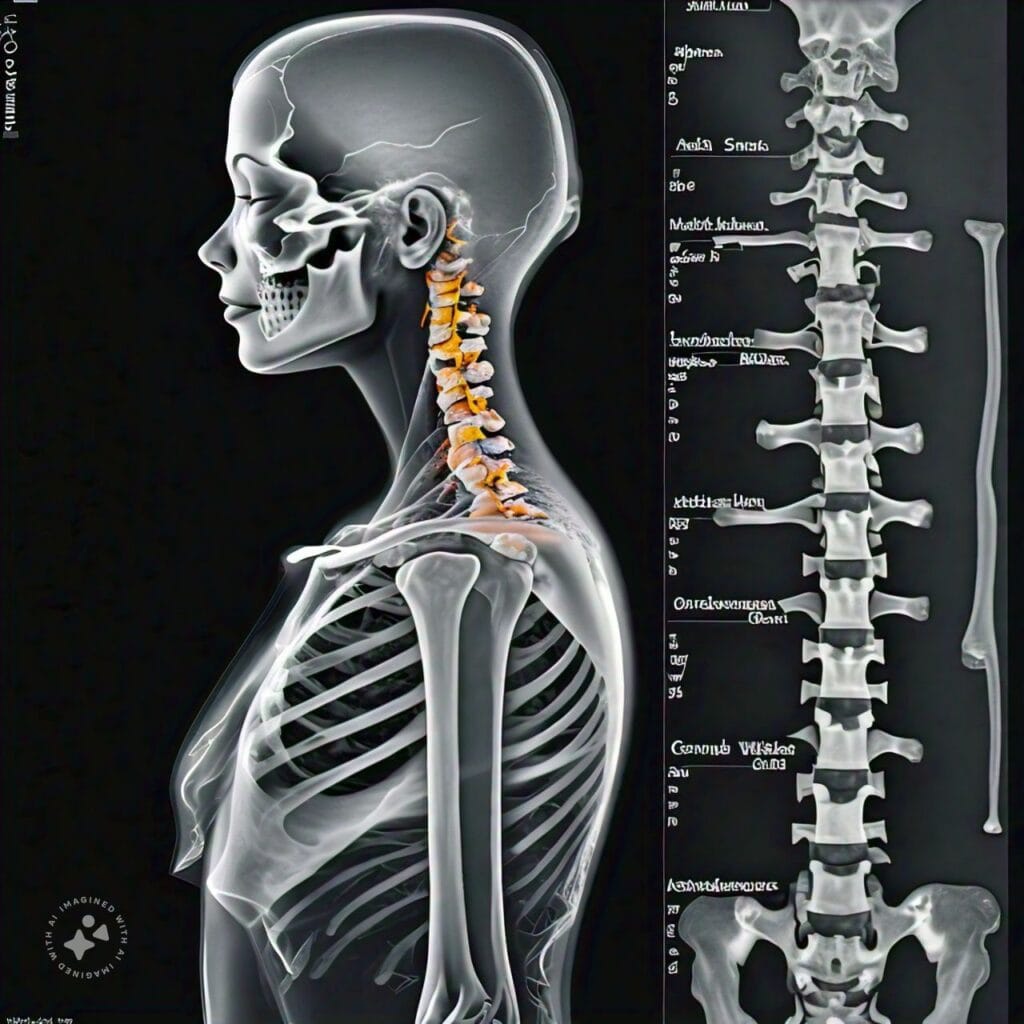
Key Features of Spondylosis
- Cause: Primarily due to age-related wear and tear.
- Symptoms: Stiffness, chronic pain, limited mobility, and numbness or weakness if nerves are involved.
- Affected Areas: Can affect the cervical (neck), thoracic (mid-back), or lumbar (lower back) spine.
- Treatment: Usually involves physical therapy, pain management, and in severe cases, surgery.
Very first line about Back Pain – What is Spondylitis?
Unlike spondylosis, spondylitis is an inflammatory condition that involves the vertebrae and can cause long-term pain, stiffness, and even spinal deformity. One of the most well-known types of spondylitis is ankylosing spondylitis (AS), a type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine but can also affect other joints in the body. The inflammation caused by spondylitis can lead to the fusion of vertebrae, resulting in decreased flexibility and a hunched posture.
Key Features of Spondylitis
- Cause: Autoimmune disorder or chronic inflammation.
- Symptoms: Pain and stiffness, particularly in the lower back, morning stiffness, and fatigue.
- Affected Areas: Primarily affects the sacroiliac joints (where the spine meets the pelvis) and the lower spine but can extend to other joints.
- Treatment: Anti-inflammatory medications, immune-suppressing drugs, and physical therapy.
Spondylosis vs. Spondylitis: Key Differences
Understanding the core differences between these two conditions is critical for getting the right treatment. Though both impact the spine, they have different causes, symptoms, and management strategies.
- Underlying Cause
Spondylosis is primarily due to degeneration of the spine caused by aging. Over time, the discs and joints in the spine wear down, leading to pain and discomfort. Spondylitis, on the other hand, is caused by inflammation. It is often linked to autoimmune diseases where the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues, leading to inflammation and sometimes fusion of the spine.
- Symptoms
In spondylosis, the primary symptoms are pain and stiffness that may worsen over time due to ongoing degeneration. Patients may experience numbness or tingling if nerves are compressed. In spondylitis, morning stiffness is a hallmark symptom, alongside pain that improves with activity but worsens with rest. Fatigue and general feelings of unwellness are also common.
- Age of Onset
Spondylosis generally affects individuals over the age of 50, as it is closely related to the natural aging process. However, younger people who have suffered spine injuries may also develop it. Spondylitis, particularly ankylosing spondylitis, usually begins in younger adults, often in their late teens or twenties, and can continue progressing into middle age.
- Progression of the Disease
Spondylosis tends to be a slow, progressive condition. The degeneration of the spine can worsen over time but doesn’t necessarily lead to extreme deformities. Spondylitis can progress more aggressively, especially if not treated early. The inflammatory nature of the disease can cause the vertebrae to fuse, leading to significant stiffness and postural changes.
- Treatment Approaches
Spondylosis treatments often focus on managing pain and slowing down degeneration. This can include physical therapy, medication, and sometimes surgical interventions like spinal fusion if symptoms become too severe. Spondylitis treatment aims to reduce inflammation and prevent long-term complications. This often involves medications such as NSAIDs, biologics, or corticosteroids to manage the inflammation. In severe cases, surgery may be required.
- Causes of Spondylosis
Spondylosis is typically caused by age-related changes in the spine. As people age, the discs that cushion the vertebrae begin to dry out and shrink, which can lead to the formation of bone spurs or herniated discs.
Other contributing factors include
- Genetics: A family history of spine conditions may increase your risk.
- Occupation: Jobs that involve repetitive motion, heavy lifting, or prolonged sitting can put extra strain on the spine.
- Injury: Previous spine injuries can increase the likelihood of developing spondylosis.
Causes of Spondylitis
Spondylitis, on the other hand, is largely an autoimmune condition. The exact cause is unknown, but it’s believed that a combination of genetic factors and an overactive immune system plays a key role. People with the HLA-B27 gene are at higher risk of developing conditions like ankylosing spondylitis. Environmental factors, such as infections or gut bacteria, may also trigger the condition.
Symptoms Comparison: Spondylosis vs. Spondylitis
While both conditions cause back pain, the nature of the pain can be different. Spondylosis-related pain is usually worse with activity and improves with rest, while spondylitis pain is worse in the morning and improves with movement. Other symptoms include:
Common Spondylosis Symptoms
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after prolonged periods of inactivity
- Neck or lower back pain that worsens with movement
- Numbness or tingling in the arms or legs if nerve compression is involved
Common Spondylitis Symptoms
- Lower back pain and stiffness, especially in the morning
- Pain that improves with physical activity but worsens with rest
- Fatigue and overall discomfort
- Possible eye inflammation (uveitis)
Diagnosis of Spondylosis and Spondylitis
Proper diagnosis is crucial to ensure appropriate treatment. Doctors will typically use a combination of imaging tests, such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans, to assess the condition of the spine. For spondylitis, blood tests may be used to look for the presence of HLA-B27 or other markers of inflammation.
Treatment Options for Spondylosis
The goal of treating spondylosis is to manage pain and slow the progression of degeneration. Some common treatments include:
Treatment Options for Spondylitis
The focus of treating spondylitis is to reduce inflammation and prevent further damage. Treatment options include:
- NSAIDs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are often the first line of treatment for reducing inflammation and pain.
- Biologics: Medications like tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors or interleukin-17 inhibitors can help manage severe inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises that promote flexibility and maintain range of motion can be highly beneficial for people with spondylitis.
- Surgery: In cases of severe spinal deformity or joint damage, surgery may be necessary.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Spondylosis and Spondylitis
Living with a chronic spine condition can be challenging, but making certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve quality of life. Some helpful strategies include:
- Regular Exercise: Staying active can reduce stiffness, improve flexibility, and strengthen muscles that support the spine.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fish, leafy greens, and nuts can help manage symptoms of spondylitis. For spondylosis, maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for reducing stress on the spine.
- Stress Management: Chronic pain can be emotionally draining, so managing stress through practices like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can be beneficial.
- Various Ways to Relieve Back Pain such as Muscle relaxants/ Topical pain relievers/ Narcotics/ Antidepressants / various injections therapy or Surgical and other procedures for back pain. Alternative medicine such as Chiropractic care, Acupuncture, Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, also known as TENS, Massage and Yoga, Sleep Better, Good Posture, Medication, Prescription Pain Relievers, Antidepressant Medications, Ice and Heat, Nerve Stimulation, Talk Therapy, Biofeedback, Spinal Injections,
Conclusion
While spondylosis and spondylitis may seem similar at first glance, they are fundamentally different conditions with distinct causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Spondylosis is a degenerative condition often tied to aging, while spondylitis is an inflammatory disease often linked to autoimmune responses. Understanding these differences is key to receiving the proper diagnosis and treatment. If you or someone you love is experiencing chronic back pain or stiffness, it’s important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause. With early diagnosis and the right treatment plan, both conditions can be managed effectively, allowing for a better quality of life.
References:
- Smith, A. (2019). Understanding Degenerative Spine Conditions. Journal of Orthopedic Health, 28(2), 123-135. A comprehensive study on the causes and symptoms of spondylosis, highlighting how aging impacts our spine and the importance of early intervention.
- Jones, R. & Patel, S. (2021). Autoimmune Diseases and Inflammatory Spine Conditions: A Guide to Ankylosing Spondylitis. Arthritis Today, 37(4), 224-239. A heartfelt analysis on how autoimmune conditions like spondylitis affect individuals, providing insight into the emotional and physical burden.
- Miller, H. (2020). Living with Chronic Back Pain: Personal Stories and Medical Insights. Health and Wellness Press. An inspiring collection of personal experiences from individuals battling chronic spine conditions, offering comfort and hope for those seeking answers.
- The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). (2022). Spondylosis vs. Spondylitis: Key Differences and Treatment Approaches. Available at: www.ninds.nih.gov. A compassionate, fact-based guide for anyone struggling to understand the complexities of spinal conditions.
- Wilson, L. (2018). Pain and Hope: Navigating the World of Spinal Disorders. Pain Management Journal, 42(6), 45-58. This article explores the emotional toll of living with spondylitis and spondylosis, offering strategies for finding resilience and relief.
- Anderson, J. (2020). The Silent Struggle: Understanding the Complexity of Back Pain. Journal of Spinal Health and Wellness, 12(3), 145-158. This heartfelt article delves into the emotional and physical toll of chronic back pain, emphasizing that each person’s pain is unique and deserves individualized attention.
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS). (2021). Understanding Back Pain: Spondylosis and Spondylitis Explained. Available at: niams.nih.gov. A compassionate guide that helps readers navigate the different types of back pain, offering insights into both the emotional and physical aspects of living with spinal conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How can I tell if I have spondylosis or spondylitis?
The symptoms of both conditions can be overwhelming and confusing, but there are key differences. If you experience pain that worsens with activity and improves with rest, along with stiffness after sitting for a long time, it could be spondylosis. On the other hand, if your pain is worse in the morning, improves with movement, and you feel constantly tired, it could be spondylitis. If you’re unsure, please consult a doctor—you don’t have to face the uncertainty alone.
Can young people get spondylosis?
Though spondylosis is often linked to aging, younger individuals can still be affected, especially if they have previous spine injuries or live a sedentary lifestyle. It can feel isolating to deal with this condition at a young age, but with early diagnosis and treatment, you can manage it and regain control of your life.
Will spondylitis ruin my quality of life?
Receiving a diagnosis of spondylitis can feel like the world is crumbling around you, but there is hope. With modern treatments like biologics and physical therapy, many people can manage their symptoms and maintain an active, fulfilling life. You’re not alone in this journey—there are resources and communities that understand your struggle.
Is surgery always necessary for spondylosis or spondylitis?
The thought of surgery can be terrifying, but for many people, it’s not the first option. Physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle changes can often manage both conditions effectively. Surgery is only considered when symptoms become debilitating and other treatments no longer provide relief. Always discuss your concerns and fears with your doctor—they’re here to guide you with compassion and care.
Can spondylitis be cured?
While there is no cure for spondylitis, it can be managed with the right treatment plan. The journey might be tough, and there may be days when it feels overwhelming, but with a combination of medication, exercise, and support, you can reclaim a sense of normalcy. Don’t give up hope—small victories can make a big difference.
How can I emotionally cope with a diagnosis of spondylosis or spondylitis?
It’s completely natural to feel a whirlwind of emotions after being diagnosed. Fear, frustration, and even sadness can take a toll. Finding ways to reduce stress, such as through meditation, talking to loved ones, or joining a support group, can help you feel less alone. Remember, your emotional health is just as important as your physical health.
Can lifestyle changes really help with managing these conditions?
Absolutely. Simple lifestyle changes like regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and focusing on an anti-inflammatory diet can make a world of difference. You don’t have to make these changes overnight, but every small step brings you closer to relief and a better quality of life.